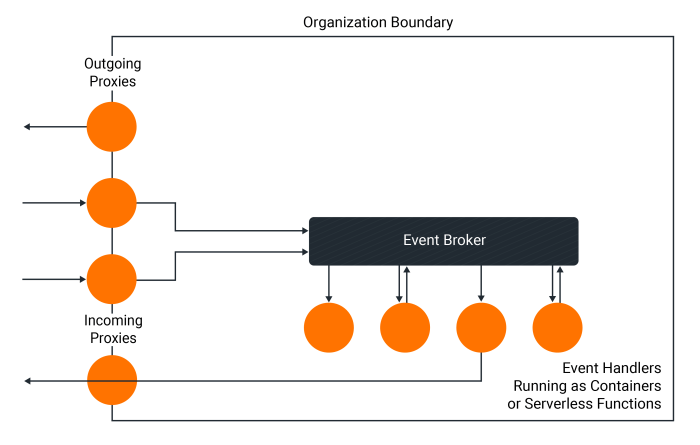
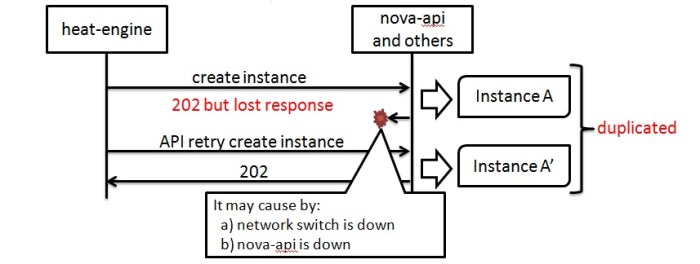
Effective disaster recovery planning is crucial for any organization. A robust plan not only protects critical data and systems but also ensures business continuity in the face of unforeseen events. This comprehensive guide details how to rigorously test your disaster recovery plan, ensuring its effectiveness and readiness.
This document provides a structured approach to testing your disaster recovery plan, covering crucial aspects like planning, testing methodologies, personnel roles, communication, and technological considerations. It also includes practical insights on Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) and vital elements like legal and regulatory compliance. The ultimate goal is to equip you with the knowledge and tools to conduct thorough and realistic disaster recovery tests.
Planning and Preparation

A robust disaster recovery plan is crucial for any organization. It Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a disruptive incident, ensuring business continuity and minimizing potential damage. Careful planning and preparation significantly mitigate the impact of unforeseen events, safeguarding valuable assets and maintaining operational stability.Developing a comprehensive disaster recovery plan involves a meticulous process of identifying potential risks, establishing communication protocols, and meticulously documenting critical systems and data.
Regular review and updates are essential to maintain the plan’s effectiveness and relevance in a dynamic environment.
Developing a Disaster Recovery Plan
A well-structured disaster recovery plan is essential for maintaining business continuity during disruptions. It Artikels the steps needed to restore operations and safeguard critical data. The development process is iterative and requires careful consideration of various factors.
- Risk Assessment: Thoroughly identify potential threats to the organization, ranging from natural disasters to cyberattacks. Consider the likelihood and potential impact of each risk, evaluating the organization’s vulnerabilities to each threat. This step is crucial for prioritizing resources and allocating appropriate mitigation strategies.
- System Inventory: Create a detailed inventory of all critical systems and data. Include hardware, software, network configurations, and data storage locations. This inventory forms the foundation for data recovery and system restoration procedures.
- Recovery Strategies: Develop detailed recovery strategies for each critical system and process. This includes outlining the steps for data backup, restoration, and system recovery. Consider both on-site and off-site recovery options. For instance, a company storing customer data in the cloud may have a different recovery strategy compared to one using on-premises storage.
- Communication Protocols: Establish clear and concise communication protocols for all personnel involved in disaster recovery. Designate roles and responsibilities, outlining the communication channels to be used during an incident. This ensures that information is disseminated effectively and efficiently.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the disaster recovery plan to ensure its effectiveness. Simulate disaster scenarios to identify potential weaknesses and refine the plan accordingly. Regular testing helps identify and address any shortcomings in the recovery process.
Key Components of a Comprehensive Disaster Recovery Plan
A robust plan incorporates several key elements to ensure successful recovery.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities to the organization. This includes natural disasters, cyberattacks, and other potential threats.
- Business Impact Analysis: Evaluating the potential impact of each risk on the organization’s operations, finances, and reputation. This analysis helps prioritize recovery efforts and allocate resources effectively.
- System Recovery Procedures: Detailed steps for restoring critical systems and applications. This includes hardware and software restoration, data recovery, and network reconfiguration.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Strategies for backing up critical data and restoring it in the event of a disaster. This includes defining backup frequency, storage locations, and recovery procedures.
- Communication Protocols: Clearly defined communication channels and procedures to keep personnel informed during a disaster. This includes establishing a chain of command and communication channels.
- Personnel Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities for personnel involved in disaster recovery. This ensures accountability and efficiency during the recovery process.
Identifying Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
A thorough risk assessment is critical to the effectiveness of a disaster recovery plan.
- Natural Disasters: Floods, earthquakes, fires, and other natural events can severely disrupt operations. A risk assessment should consider the frequency and severity of these events in the organization’s geographic location.
- Cyberattacks: Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and denial-of-service attacks pose significant threats to sensitive data and business operations. Organizations should consider the likelihood of these attacks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
- Human Error: Mistakes or negligence by employees can also lead to significant disruptions. The plan should address procedures for preventing and managing human errors.
- Technological Failures: System failures, hardware malfunctions, and software glitches can disrupt operations. The plan should consider strategies for maintaining system uptime and minimizing downtime.
Best Practices for Communication Protocols
Effective communication is essential during a disaster.
- Establish a communication center: A designated communication center will facilitate the coordination and dissemination of information during a disaster. This center should have backup power and communication lines.
- Develop a communication plan: Clearly Artikel the roles and responsibilities of personnel involved in disaster communication. This plan should specify the communication channels to be used in different scenarios.
- Regular training: Regular training for all personnel involved in disaster communication is essential to ensure familiarity with procedures and communication channels.
- Use multiple communication channels: Leverage multiple communication channels such as phone, email, text messaging, and social media to ensure wide reach.
Documenting Critical Systems and Data
A detailed inventory of critical systems and data is essential for a successful recovery.
| System/Data | Description | Backup Location | Recovery Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Database | Stores customer information | Cloud storage | Restore from cloud storage |
| Sales Management System | Manages sales data | On-site backup | Restore from on-site backup |
| Inventory Management System | Tracks inventory levels | Cloud storage and on-site backup | Restore from cloud storage or on-site backup |
Regular Review and Update Checklist
Regular reviews are essential to ensure the plan’s relevance and effectiveness.
- Review the risk assessment regularly to identify emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Update the inventory of critical systems and data to reflect changes.
- Review and update recovery procedures to address evolving technological needs.
- Review and update communication protocols to reflect current communication technologies.
- Test the plan periodically to identify any weaknesses and address them.
Testing Methodology
Thorough testing of disaster recovery (DR) plans is crucial for ensuring their effectiveness in a crisis. Properly designed and executed tests provide valuable insights into potential weaknesses and allow for adjustments before a real disaster occurs. This section details various testing methods, comparing approaches, emphasizing the importance of realistic scenarios, and outlining personnel involvement and evaluation criteria.Testing disaster recovery procedures goes beyond simply reviewing documents.
It requires practical application and analysis to validate the plan’s ability to restore operations within the defined recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs).
Various Testing Methods
Testing disaster recovery procedures can encompass a range of methods, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. A comprehensive approach often combines multiple techniques to provide a holistic assessment of the plan’s efficacy.
- Simulations: Simulations create a simulated disaster environment, replicating aspects of a real-world event. These tests allow for a controlled environment to evaluate the response time and effectiveness of the DR procedures. Examples include network outages, data center failures, or natural disasters, enabling teams to practice their roles and procedures in a controlled environment.
- Tabletop Exercises: Tabletop exercises are a more structured approach, involving key personnel in a discussion-based scenario. Participants discuss and make decisions regarding the recovery process. They are useful for identifying potential bottlenecks and communication issues in a low-pressure setting. This method is highly beneficial for evaluating the plan’s feasibility and identifying areas needing improvement.
- Walkthroughs: Walkthroughs are less intensive than simulations or tabletop exercises. They involve a review of the DR plan’s procedures, often using a checklist-based approach. The focus is on verifying the steps involved in the recovery process. These are valuable for identifying gaps in the plan’s documentation or implementation.
- Pilot Tests: Pilot tests involve implementing a small portion of the DR plan, such as a specific application or data center component, in a controlled environment. This allows for a more realistic evaluation of the plan’s feasibility and identifies potential problems before full-scale implementation. This method helps to ensure that the recovery processes are functioning smoothly and accurately.
Comparison of Testing Approaches
Different testing approaches offer varying levels of detail and realism. Simulations offer a more comprehensive evaluation, while tabletop exercises allow for a deeper discussion of recovery strategies. Walkthroughs provide a basic review of procedures, while pilot tests focus on specific components of the plan.
Importance of Realistic Scenarios
Realistic scenarios are essential in disaster recovery testing. Focusing solely on hypothetical scenarios or oversimplifying real-world conditions will not accurately reflect the challenges faced during an actual disaster. For instance, testing for a power outage in a data center should consider factors such as the complexity of the power backup systems, the time required for switching over, and the impact on various applications and services.
Involving Key Personnel
Effective testing requires the involvement of key personnel across different departments. This includes IT staff, operations managers, security personnel, and executives. Clear roles and responsibilities should be defined, and personnel should be adequately trained in the recovery procedures. Their involvement ensures that all aspects of the plan are considered and tested.
Criteria for Evaluating Effectiveness
The effectiveness of testing should be evaluated based on predefined criteria, such as:
- Time to Recovery: How quickly can critical systems and data be restored?
- Data Loss: What is the acceptable level of data loss during the recovery process?
- Personnel Response: How effectively do personnel execute the recovery procedures?
- Communication Efficiency: How effectively does the team communicate during the recovery process?
Documenting Test Results
A structured framework for documenting test results is essential. This framework should include:
- Date and Time of Test: Critical for tracking and analysis.
- Type of Test: (e.g., simulation, tabletop exercise).
- Scenario Description: A detailed description of the simulated event.
- Personnel Involved: A list of participants.
- Results: A summary of the test outcomes, including any issues or problems encountered.
- Corrective Actions: Recommendations for improving the DR plan based on test results.
System and Data Recovery
A robust disaster recovery plan hinges on the ability to quickly and effectively restore systems and data after a disruption. This section delves into the critical aspects of system recovery, data backup and restoration, data recovery site establishment, and the paramount importance of data integrity in disaster scenarios. Effective procedures are essential to minimize downtime and business impact.System and data recovery is a crucial component of a comprehensive disaster recovery strategy.
It encompasses the steps needed to restore operational systems and retrieve critical data following a disruptive event. This includes not only the technical processes but also the organizational procedures and policies that support a smooth and rapid recovery.
System Recovery Plan Design
A well-defined system recovery plan details the steps required to restore individual systems to operational status. This involves identifying critical systems, determining recovery time objectives (RTOs), and outlining the specific procedures for each system. Different systems require tailored approaches. For example, a database server recovery plan will differ from a web server recovery plan.
- Database Servers: Recovery plans for database servers often involve restoring backups to a replica environment. This could involve using a cloud-based backup solution or a dedicated recovery server. The plan should also include steps for validating data integrity after restoration. This might include comparing data checksums, or running data consistency checks.
- Web Servers: Web server recovery plans often focus on restoring website functionality. This might include restoring application code, configurations, and database connections. The plan should consider the availability of external services and the necessary configurations to restore the website’s accessibility.
- Application Servers: Application server recovery plans should Artikel steps to restore the application software, configurations, and associated data. This might involve restoring the server’s operating system, installing application software, and reconfiguring database connections. Recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) should be defined to establish the acceptable recovery time and data loss tolerance.
Data Backup and Restoration Procedures
Comprehensive data backup and restoration procedures are essential for minimizing data loss. These procedures must be regularly tested and updated to ensure effectiveness. A crucial aspect is determining the appropriate backup frequency and data retention policies.
- Backup Frequency: The frequency of backups depends on the criticality of the data and the acceptable data loss tolerance. Frequent backups minimize the amount of data lost in case of a disaster. Daily backups are common for critical data, while less frequent backups may suffice for less crucial data.
- Backup Types: Different backup types (full, incremental, differential) offer varying degrees of efficiency and recovery time. A combination of backup types can be used to optimize backup efficiency and minimize data loss.
- Restoration Procedures: Restoration procedures must be detailed and well-documented. Clear instructions on how to restore data from backups should be available. The plan should Artikel the steps to restore data to the original or a recovery environment.
Data Recovery Site and Procedures
Establishing a separate data recovery site is crucial for disaster recovery. This site serves as a secondary location for storing backups and restoring systems in the event of a primary site failure. A well-defined data recovery site must be physically separated from the primary site.
- Physical Separation: The recovery site should be geographically separate from the primary site to minimize the risk of shared vulnerabilities. This separation reduces the impact of a disaster affecting both sites.
- Infrastructure Replication: The recovery site should have a similar infrastructure to the primary site, including hardware, software, and network configurations. This facilitates a faster and more efficient restoration process.
- Recovery Procedures: Recovery procedures at the secondary site must be well-defined. This includes protocols for activating the recovery site, restoring data, and testing the recovery process.
Data Integrity and Recovery Significance
Data integrity is paramount during disaster scenarios. Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data after recovery is critical to business continuity. Data recovery should not compromise data integrity.
Data Protection and Security Best Practices
Protecting data requires implementing robust security measures. These include access controls, encryption, and regular security audits. This safeguards against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest enhances security. This ensures that data is protected even if it is compromised during transmission or storage.
- Access Controls: Implementing strong access controls limits access to sensitive data to authorized personnel. This minimizes the risk of data breaches and unauthorized modifications.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits helps identify and address vulnerabilities. This ensures that security measures remain effective and protect data against emerging threats.
Importance of Clear Data Recovery Procedures
Clearly defined data recovery procedures are essential for a smooth and efficient restoration process. These procedures must be well-documented and regularly tested.
Communication and Coordination
Effective communication and coordination are critical components of a robust disaster recovery plan. Clear, timely communication with all stakeholders—internal and external—is paramount for a swift and successful recovery. A well-defined communication strategy minimizes confusion, ensures efficient resource allocation, and fosters collaboration among various teams and support organizations.
Communication Strategies for Stakeholders
Effective communication strategies are crucial for a smooth disaster recovery process. These strategies are designed to ensure that critical information is disseminated accurately and promptly to all stakeholders, minimizing confusion and maximizing efficiency. A well-defined plan should cover both internal and external communication needs.
- Internal Communication: Internal communication channels should be clearly established and tested beforehand. This includes designated communication channels for different teams, such as email lists, instant messaging platforms, and dedicated communication hubs. For instance, establishing a dedicated Slack channel or a secure messaging app can facilitate rapid updates and crucial information exchange during the recovery period.
- External Communication: External communication protocols should be established for communicating with customers, partners, regulatory bodies, and the media. This includes designating spokespersons, developing pre-approved statements, and outlining protocols for responding to inquiries. For example, having a pre-defined press release template ready can expedite the process of conveying information to the public during a crisis.
Importance of Clear Communication During a Disaster
Clear communication during a disaster is essential for maintaining order and ensuring a coordinated response. Ambiguity and delays can lead to increased damage, confusion, and inefficiencies. Clear communication streamlines decision-making, fosters collaboration, and enables stakeholders to effectively contribute to the recovery effort.
- Reduced Confusion and Errors: Clear communication minimizes misunderstandings and misinterpretations, which can lead to critical errors during the recovery process. This is especially important in stressful situations.
- Improved Coordination: Clear communication channels ensure that all relevant parties are informed and aligned, enabling better coordination among different teams and support organizations.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Confidence: Timely and transparent communication builds trust and confidence among stakeholders. This is especially important for maintaining public relations and restoring business operations.
Methods for Coordinating with External Support
Effective coordination with external support during a disaster is crucial for maximizing resources and expertise. Establishing clear communication channels and protocols in advance can significantly improve the efficiency of the recovery process.
- Pre-identified Contacts: Establishing a list of pre-identified contacts within external support organizations (e.g., IT service providers, legal counsel) ensures that communication channels are readily available in case of an incident. This pre-planning can save critical time.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Defining clear Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with external support providers can Artikel their responsibilities and expected response times, ensuring accountability and a structured approach to recovery.
- Regular Communication and Updates: Establishing a system for regular communication and updates with external support providers, outlining the status of the recovery effort and resource needs, is crucial. For example, holding regular conference calls to provide updates and ensure alignment on the recovery strategy.
Importance of Accurate and Timely Information Dissemination
Accurate and timely information dissemination is critical during a disaster recovery process. Inaccurate or delayed information can exacerbate the crisis, causing confusion and impacting the effectiveness of the recovery.
- Minimizing Panic and Speculation: Accurate and timely information minimizes speculation and panic among stakeholders. This is especially important during a crisis.
- Facilitating Effective Decision-Making: Accurate and timely information allows for informed decision-making by all stakeholders. This can help minimize further damage and ensure an efficient recovery process.
- Maintaining Public Trust: Consistent and accurate communication with the public is crucial for maintaining trust during a disaster. This is especially important for organizations seeking to restore public confidence after an incident.
System for Tracking and Monitoring the Disaster Recovery Process
A robust system for tracking and monitoring the disaster recovery process is essential for maintaining control and accountability. This system should provide visibility into the status of different recovery tasks, resource allocation, and timelines.
- Tracking Tools: Implementing dedicated tools for tracking the progress of recovery tasks, identifying bottlenecks, and monitoring the status of critical systems is crucial. Project management software or specialized disaster recovery tracking tools can assist in this process.
- Progress Reporting: Regular progress reports, outlining the status of recovery tasks and identifying any potential delays or roadblocks, are crucial. This reporting mechanism should involve key stakeholders.
- Metrics and KPIs: Defining key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring the effectiveness of the recovery process is essential. This allows for objective assessment of progress and adjustments to the recovery plan as needed.
Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO)

Defining Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) is crucial for establishing realistic and achievable disaster recovery goals. These metrics quantify the acceptable downtime and data loss following a disaster, guiding the development and testing of recovery procedures. Understanding and effectively communicating RTO and RPO values ensures alignment between business needs and technical capabilities.Establishing these objectives is not simply about technical specifications; it’s about understanding the impact of downtime and data loss on business operations and customer satisfaction.
This understanding allows for the development of recovery strategies that balance the need for swift recovery with the need to minimize data loss.
Determining Appropriate RTO and RPO Values
Appropriate RTO and RPO values are determined by considering the criticality of the affected systems and the potential financial and operational consequences of downtime or data loss. Factors like the nature of the business, the industry standards, and the specific business functions supported by the system need to be carefully considered. A thorough risk assessment is essential in identifying the potential impact of disruptions.
RTO and RPO Calculation Methods
Various methods can be employed to calculate RTO and RPO values. One approach involves analyzing historical data on system downtime and data loss events, allowing for the estimation of potential future disruptions. Another method focuses on the criticality of the data and the systems, assigning higher RTO and RPO values to mission-critical systems. Statistical modeling and simulation tools can also be used to predict and model the potential impact of various disaster scenarios.
Example: A financial institution might establish a lower RTO for its transaction processing system than for a reporting system, recognizing the immediate impact of transaction delays on customers and revenue. Conversely, a manufacturing company may prioritize maintaining access to critical production data, resulting in a lower RPO for its manufacturing systems.
Relationship Between RTO and RPO
RTO and RPO are intrinsically linked and often have an inverse relationship. Lower RTO values usually correlate with lower RPO values, as faster recovery often means a higher risk of losing recent data. Conversely, systems requiring minimal downtime may need to accept a higher level of acceptable data loss. This trade-off needs to be carefully evaluated to find a balance that satisfies business needs.
Establishing Realistic RTO and RPO Goals for Different Systems
Realistic RTO and RPO goals must be established for each system based on its criticality and the impact of its failure. A clear understanding of the operational dependencies and business processes supported by each system is necessary. For example, systems supporting customer-facing operations might require much tighter RTO and RPO values than systems used for internal reporting or analysis.
Balancing RTO and RPO to Meet Business Needs
Balancing RTO and RPO is a critical aspect of disaster recovery planning. Strategies should focus on minimizing the negative impact of both downtime and data loss. The choice between faster recovery and minimizing data loss should be carefully considered, aligning with business needs and regulatory requirements. For example, a company might choose a longer RPO if it enables a faster RTO to minimize operational disruptions.
Communicating RTO and RPO Goals Effectively to Stakeholders
Effective communication of RTO and RPO goals is vital to ensure alignment and buy-in from all stakeholders. Clear and concise documentation of the goals, along with explanations of the rationale behind them, is essential. Regular communication and updates to stakeholders about the progress of the recovery plan are also necessary. Training sessions can educate stakeholders on the importance of RTO and RPO and how they affect business operations.
Technology and Infrastructure

Robust disaster recovery hinges on a resilient technological foundation. A well-structured technological infrastructure ensures the organization’s ability to quickly recover critical systems and data following a disruption. The selection and implementation of appropriate technologies are crucial for achieving swift recovery and minimizing business impact.A thorough understanding of the specific technological needs and the diverse array of available solutions are essential for successful disaster recovery planning.
This includes a careful consideration of both on-premises and cloud-based solutions, balancing cost-effectiveness with reliability and scalability.
Importance of Reliable Infrastructure
Reliable infrastructure forms the bedrock of a successful disaster recovery strategy. A robust network, efficient storage, and redundant systems are vital for maintaining operations during and after a disruption. Unreliable infrastructure can lead to extended downtime, significant financial losses, and damage to the organization’s reputation. This highlights the importance of proactive measures to ensure the integrity and dependability of the infrastructure.
Selection Criteria for Disaster Recovery Technologies
Several key criteria should guide the selection of disaster recovery technologies. These include factors such as cost-effectiveness, scalability, compatibility with existing systems, and ease of implementation and maintenance. Security features, data protection measures, and vendor support are also critical considerations. The chosen technologies must align with the organization’s specific recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs).
Role of Cloud Computing in Disaster Recovery
Cloud computing offers significant advantages in disaster recovery. Cloud-based solutions provide scalable resources, enabling organizations to rapidly deploy and scale resources during a crisis. Cloud storage options facilitate the quick restoration of data, minimizing downtime and enabling business continuity. The inherent redundancy and geographical distribution of cloud platforms are valuable in mitigating the risks of localized failures.
Examples of Disaster Recovery Solutions for Different Industries
Different industries have unique disaster recovery needs. Financial institutions, for instance, often utilize specialized solutions for handling sensitive data and maintaining regulatory compliance. Healthcare organizations may prioritize solutions that safeguard patient data and ensure the continuous availability of critical medical equipment. Manufacturing companies may focus on technologies that allow for rapid restoration of production lines. The specific requirements and solutions vary significantly depending on the sector’s unique needs and regulatory landscape.
Disaster Recovery Infrastructure Types
Disaster recovery infrastructure encompasses various components. On-site backup systems, such as redundant servers and data centers, are essential. Off-site backup solutions, like cloud storage and remote data centers, provide critical data protection and recovery options. The selection of infrastructure types should align with the organization’s specific needs, considering the potential for localized disruptions.
Redundant Systems and Data Centers
Redundant systems and geographically dispersed data centers are critical components of a robust disaster recovery plan. These strategies ensure business continuity by providing backup capabilities in the event of a primary site failure. This approach minimizes the impact of disruptions, safeguarding critical operations and data. Redundancy significantly enhances the overall reliability and resilience of the disaster recovery infrastructure.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring a robust disaster recovery plan involves more than just technical aspects. A critical component is adhering to legal and regulatory requirements, particularly concerning data privacy and security. Failing to meet these standards can lead to significant penalties and reputational damage. Therefore, careful consideration of legal and regulatory compliance is paramount throughout the entire disaster recovery planning process.Understanding and proactively addressing legal and regulatory frameworks is vital for organizations to mitigate risks and maintain business continuity.
Organizations must be prepared to demonstrate their compliance with these requirements during a disaster, ensuring that the recovery process itself adheres to all applicable laws and regulations.
Legal Requirements for Disaster Recovery
Legal requirements for disaster recovery vary widely depending on industry, location, and specific regulations. Organizations must identify and understand the applicable laws and regulations in their jurisdiction, including data protection, privacy, and industry-specific mandates. This involves a thorough legal review to determine which laws and regulations are relevant and how they affect the disaster recovery plan.
Data Privacy in Disaster Recovery
Data privacy is a critical aspect of disaster recovery planning. Protecting sensitive data during a disaster is paramount. Organizations must ensure that their disaster recovery procedures adhere to data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA, depending on their industry and geographic location. Robust security measures are essential throughout the entire recovery process, from data backup and restoration to employee access controls.
These procedures must be carefully documented and reviewed to ensure compliance.
Ensuring Compliance During a Disaster
Ensuring compliance during a disaster requires meticulous planning. Disaster recovery plans should explicitly address compliance requirements. For example, a clear protocol for data encryption and access control during recovery is crucial. Documentation of compliance activities and procedures is essential for demonstrating adherence to regulations after the disaster.
Role of Legal Counsel in Disaster Recovery Planning
Legal counsel plays a vital role in disaster recovery planning. Legal professionals can provide guidance on identifying and understanding applicable regulations, drafting compliance procedures, and ensuring that the plan is legally sound. They can also advise on potential liabilities and risks, helping organizations develop proactive strategies for managing compliance during a disaster. Their input ensures the plan is legally robust and minimizes potential legal issues.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements by Industry
Different industries have specific regulatory compliance requirements that impact disaster recovery. For example, healthcare organizations must adhere to HIPAA regulations, while financial institutions must comply with regulations specific to financial data security. These requirements dictate the levels of security, backup procedures, and recovery time objectives (RTOs) needed to protect sensitive information. Understanding and meeting these industry-specific needs is essential for the success of a disaster recovery plan.
This requires a deep understanding of each industry’s specific regulatory framework.
| Industry | Key Regulatory Requirements |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | HIPAA, state-specific regulations |
| Finance | PCI DSS, GLBA, state-specific regulations |
| Education | FERPA, state-specific regulations |
| Government | Specific federal, state, and local regulations |
Importance of Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Legal and regulatory considerations are integral to a successful disaster recovery plan. Ignoring these factors can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions. A robust plan considers the specific regulations applicable to the organization, ensuring that all recovery procedures are compliant. This proactively mitigates risks and ensures a smooth recovery process. The plan should include provisions for compliance monitoring and audits throughout the process.
Budget and Resources
A robust disaster recovery plan hinges on a realistic budget and the effective allocation of resources. Proper planning ensures sufficient funding for essential components, from hardware and software to personnel training and testing. This section details the critical aspects of estimating costs, allocating budgets, tracking expenditures, and performing cost-benefit analysis for optimal disaster recovery investments.Effective disaster recovery is not just about having a plan; it’s about having the financial resources to execute it.
A well-defined budget ensures that the organization has the necessary funds for all stages of recovery, from immediate response to long-term restoration. This includes considering potential contingencies and ensuring the plan is adaptable to unforeseen circumstances.
Estimating Disaster Recovery Costs
Accurately estimating the costs of disaster recovery is crucial for effective planning and securing necessary funding. This involves considering various factors, including the potential scope of the disaster, the recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs), the required hardware and software, personnel costs, and potential legal or regulatory compliance costs. Detailed assessments of existing infrastructure, including data storage, backup systems, and communication networks, are essential.
A thorough inventory of assets and data, along with an analysis of potential service disruptions, will provide a comprehensive picture of the costs associated with recovery. Understanding the specific disaster scenarios and their potential impact on the organization will allow for more accurate cost estimations.
Importance of Allocating Sufficient Budget
Adequate funding for disaster recovery is essential to ensure a swift and successful recovery. A sufficient budget ensures that the organization has the resources to acquire the necessary technology, train personnel, and execute the plan effectively. Insufficient funding can lead to delays, inefficiencies, and potentially insurmountable obstacles during a disaster. Failure to allocate sufficient resources can jeopardize the organization’s ability to resume operations and potentially cause irreparable damage to its reputation and financial standing.
Disaster Recovery Budget Template
A structured budget template is beneficial for organizing and tracking disaster recovery costs. This template should include sections for personnel costs, hardware and software expenses, data recovery and restoration costs, testing and training costs, and contingency funds. Specific costs for each component of the plan should be estimated and included, with consideration for potential increases due to inflation or unexpected expenses.
This template should be adaptable to different types of disasters and recovery scenarios.
- Personnel Costs: Salaries, overtime pay, and other compensation for personnel involved in the recovery process.
- Hardware and Software Costs: Expenses for new or replacement hardware, software licenses, and related maintenance.
- Data Recovery and Restoration Costs: Cost of recovery software, storage media, and personnel for data restoration.
- Testing and Training Costs: Expenses for disaster recovery plan testing, staff training, and related documentation.
- Contingency Funds: A dedicated reserve for unforeseen expenses or changes in the recovery plan.
Tracking and Managing Disaster Recovery Expenditures
Effective tracking and management of disaster recovery expenditures are essential for accountability and adherence to the budget. A dedicated system for recording and reporting expenditures, along with regular reviews of budget adherence, is critical. This allows for timely adjustments to the budget as needed and helps identify areas where costs can be reduced without compromising the effectiveness of the plan.
Implementing a system for tracking and managing expenditures will aid in the evaluation of the plan’s efficiency and effectiveness over time.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Disaster Recovery Investments
A cost-benefit analysis is a crucial tool for evaluating the financial viability of disaster recovery investments. This analysis assesses the potential costs of a disaster against the projected benefits of implementing and maintaining the disaster recovery plan. It involves quantifying the potential financial losses from a disaster, estimating the costs of the recovery plan, and calculating the overall return on investment.
This analysis will provide a framework for understanding the potential financial implications of various recovery scenarios. Understanding the financial implications of not having a disaster recovery plan should also be part of the analysis.
Examples of Allocating Resources Effectively
Effective resource allocation in disaster recovery requires a thoughtful approach. Consider allocating a specific budget for regular testing and training of personnel, thereby enhancing preparedness and efficiency. Another example is investing in redundant systems and data storage facilities to minimize downtime. Additionally, establishing clear communication channels and protocols is crucial, as effective communication can greatly reduce the impact of a disaster.
Prioritizing investments based on risk assessment will help focus resources where they are most needed.
- Regular Testing and Training: Dedicated budget for disaster recovery drills and staff training ensures personnel are proficient in executing the plan during an actual event.
- Redundant Systems and Data Storage: Investing in redundant systems and offsite data storage reduces the risk of data loss and downtime during a disaster.
- Clear Communication Channels: Establishing clear communication channels and protocols allows for efficient communication between stakeholders during a crisis, enabling faster response and recovery.
Post-Disaster Recovery
A comprehensive disaster recovery plan encompasses not only the preparation and testing phases, but also the critical post-disaster recovery process. This phase ensures a smooth and efficient resumption of operations, minimizing disruption and maximizing the organization’s ability to bounce back from adversity. Successfully navigating this stage hinges on a well-defined plan and a proactive approach.
Resuming Operations
After a disaster, the immediate priority is to assess the damage and implement measures to safeguard personnel and resources. This includes ensuring the safety and well-being of employees and establishing a secure and stable operational environment. Critical infrastructure and systems need to be evaluated for functionality and integrity. A prioritized approach to restoration is essential, focusing on those systems and processes that are vital for immediate business continuity.
Business Continuity and Recovery Plan
The business continuity and recovery plan provides a roadmap for resuming operations. This plan should detail specific actions to be taken in various disaster scenarios. Key components include alternative work locations, communication protocols, and resource allocation. Clear roles and responsibilities should be defined for each individual or team involved in the recovery process.
Post-Disaster Recovery Assessment
A thorough post-disaster recovery assessment is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of the disaster recovery plan. This assessment should identify the actual impact of the disaster, comparing it with the predicted impact Artikeld in the plan. Areas of success and failure should be documented, along with the reasons for both. This data informs improvements to future plans. This detailed analysis serves as a benchmark for future disaster recovery exercises and enhances the organization’s resilience.
Evaluating Disaster Recovery Plan Effectiveness
Evaluating the disaster recovery plan’s effectiveness requires a systematic comparison of the planned response with the actual response during a disaster event. Key metrics to consider include the time taken to restore critical systems, the level of data loss, and the extent of disruption to business operations. Quantifiable data points, such as recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs), provide a structured way to measure performance against expectations.
Identifying Lessons Learned and Improving the Plan
Post-disaster recovery assessments reveal valuable insights into the plan’s strengths and weaknesses. Identifying lessons learned from the experience helps to refine the disaster recovery plan, incorporating improvements for future events. This might involve upgrading technology, strengthening communication protocols, or refining the allocation of resources. Analyzing the specific challenges encountered and adapting the plan to address them strengthens the organization’s overall resilience.
Re-establishing Operations
Re-establishing operations after a disaster is a multi-faceted process. It requires careful planning and execution, encompassing the restoration of critical systems, the recovery of data, and the reintegration of personnel. The plan should specify a phased approach to operations resumption, prioritizing critical functions and gradually expanding coverage to other areas of the business. This careful and measured approach helps to minimize disruption and ensure a swift return to normalcy.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, testing your disaster recovery plan is not a one-time event, but an ongoing process that requires meticulous planning, realistic simulations, and continuous improvement. By following the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can significantly enhance your organization’s resilience and preparedness for potential disruptions. A well-tested plan is a vital investment in your organization’s future.
FAQ
What are the different types of disaster recovery testing methods?
Common testing methods include simulations, tabletop exercises, and walk-throughs. Simulations mimic real-world disaster scenarios, while tabletop exercises involve discussions among key personnel. Walk-throughs are less intensive and focus on reviewing procedures.
How often should disaster recovery plans be tested?
The frequency of testing depends on various factors, including the criticality of the systems, the potential risk of disaster, and the organization’s resources. However, it’s generally recommended to conduct tests at least annually, or more frequently if necessary.
What are Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO)?
RTO is the maximum acceptable time to restore critical systems and operations after a disaster, while RPO is the maximum acceptable data loss. Establishing realistic RTO and RPO values is essential to define the scope and expectations of the disaster recovery plan.
How do I involve key personnel in disaster recovery testing?
Involve key personnel early in the planning and testing phases. This will help ensure buy-in, understanding, and familiarity with the disaster recovery plan. Assign specific roles and responsibilities to each team member to ensure smooth execution during the test.